Major Risk Factor For Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
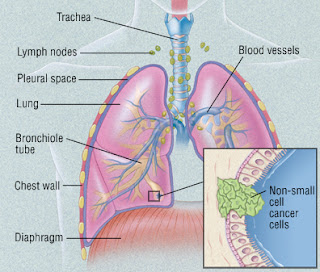
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of #lungcancer. It usually grows and spreads more slowly than small cell lung cancer. Each type of non-small cell lung cancer has different kinds of cancer cells. The cancer cells of each type grow and spread in different ways.
There are 3 common types of NSCLC:
- Squamous cell carcinoma: Cancer that begins in squamous cells, which are thin, flat cells that look like fish scales. This is also called epidermoid carcinoma.
- Large cell carcinoma: Cancer that may begin in several types of large cells.
- Adenocarcinoma: Cancer that begins in the cells that line the alveoli and make substances such as mucus.
Smoking is the major risk factor for non-small cell lung cancer
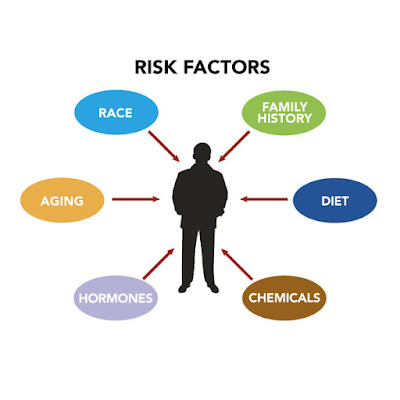
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn't mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk for lung cancer.
Risk factors for lung cancer include the following:
1. Smoking cigarettes, pipes, or cigars, now or in the past. This is the most important risk factor for lung cancer. The earlier in life a person starts smoking, the more often a person smokes, and the more years a person smokes, the greater the risk of lung cancer.2. Being exposed to secondhand smoke.
3. Being exposed to asbestos, chromium, nickel, beryllium, arsenic, soot, or tar in the workplace.
4. Living where there is air pollution.
5. Having a family history of lung cancer.
6. Being infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
7. Taking beta carotene supplements and being a heavy smoker.
Generic Ceritinib 150mg capsules which is used to treat non-small cell lung cancer.
Drug type:
Ceritinib is a targeted therapy. It is an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
What this drug is used for:
For the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer that is caused by a defect in a gene called ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase).
Drug type:
Ceritinib is a targeted therapy. It is an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
What this drug is used for:
For the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer that is caused by a defect in a gene called ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase).


Comments
Post a Comment